Application Process ID aka PID on Windows is useful for several reasons. It is mostly used to manage running processes on the system. The operating system uses PIDs to track and manage the resources used by each process, including memory, CPU, and I/O. PIDs can also terminate processes that are not responding or causing problems.
So, overall, PIDs are a fundamental part of managing and troubleshooting processes on a Windows operating system, and they play a critical role in maintaining the stability, performance, and security of the system.

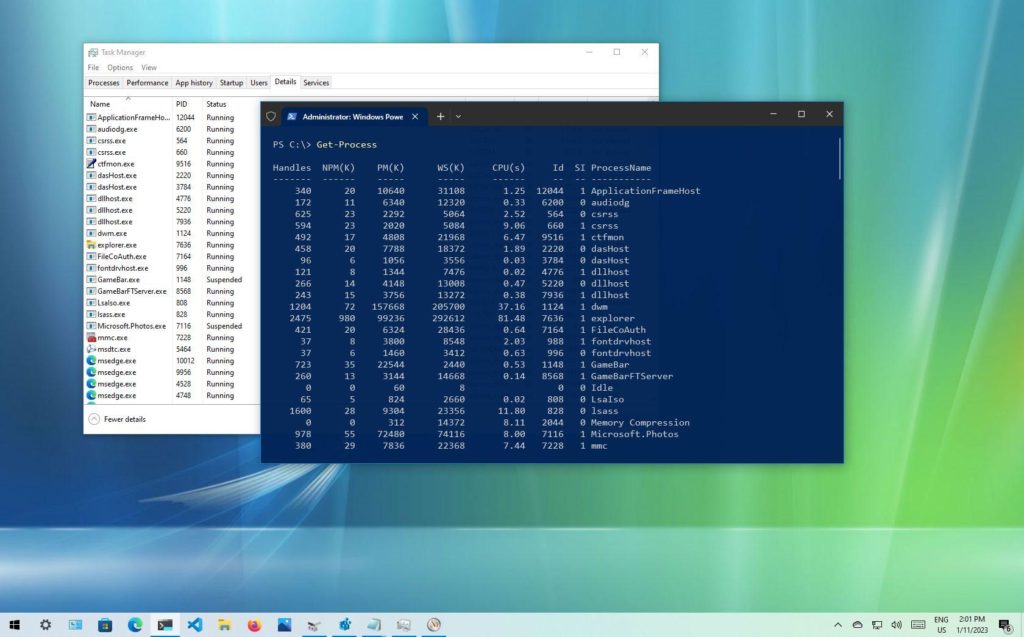
Wondering how to find the application process ID on Windows 11? We’ve got you covered. In this post, we have listed a variety of methods that you can use to find PID on your device.
Let’s get started.
What is An Application Process ID (PID)?
An Application Process ID (PID) is a unique identification number assigned to each running process on a Windows operating system. It is a number that identifies a specific instance of a program or application currently running in memory.
Each process that runs on Windows is assigned a PID by the operating system, which helps the system to manage the processes and resources more efficiently. PIDs can be viewed and managed using various system tools such as the Task Manager, Resource Monitor, or command-line tools like “tasklist” and “taskkill.”
PIDs are used by Windows to track and manage the memory, CPU, and other resources used by each process. They also help identify and troubleshoot issues related to specific processes or applications.
How to find the Application Process ID on Windows 11?
Here are some simple methods that you can use for identifying PID on your device.
Method 1: Use the Task Manager
Well, yes, here comes one of the quickest easy to find application process IDs on a Windows PC.
Press the Control + Shift+ Escape key combination to open the Task Manager app. Alternatively, you can also use the Win + X shortcut and select “Task Manager” from the context menu. In the Task Manager window, switch to the “Details” tab with a three-horizontal lines icon.
In the next window, you will be able to see the application process ID of each process under a dedicated “PID” column.
The PID is usually not displayed in the “Processes” tab of Task Manager. However, if you want this column to always show up, here’s what you need to do.
Switch to the “Processes” tab and right-click on any column and select “PID”.
Once you select it, PID will always appear on the Processes tab each time your launch the Task Manager app.
Also read: Task Manager not Working on Windows 11? Here’s the Fix!
Method 2: Use the Resource Monitor App
You can find the Application Process ID (PID) of a running process using the Resource Monitor on a Windows operating system by following these steps:
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box and type “resmon” in the Run dialog box and press Enter. This will open the Resource Monitor.
- In the Resource Monitor, go to the CPU tab.
- Under the “Processes” section, locate the process for which you want to find the PID.
- Once you have located the process, the PID will be displayed in the “PID” column next to the process name.
- Note down the PID number for the process you are interested in.
That’s it! You have now found the Application Process ID (PID) of a running process using the Resource Monitor on a Windows operating system.
Also read: How To Fix Disk Stuck at 100% in Windows Task Manager
Method 3: Command Prompt
Yes, you can also use the Terminal app to find the PID of a specific process. Follow these quick steps to get started.
- Open the Command Prompt app on your device in admin mode. Tap on the search icon placed on the Taskbar and type “Command Prompt”. Select the “Run as administrator” option.
- In the Command Prompt window, type “tasklist” and press Enter. This will display a list of all running processes on your system.
- Find the process for which you want to find the PID in the list, and note down the name of the process.
- Also, if the tasklist command output appears to be lengthy and difficult to read, especially when there are many running processes, here’s something you can do. To make it easier to navigate the results, you can copy them to a text file.
- To do this, open the Command Prompt and type the following command:
tasklist > D:\PIDfile.txt
- After you run this command, you can open the text file in any text editor to view and search the results more easily.
Also read FIX: There Are No Startup Items to Display in Task Manager Error (Windows 11)
Method 4: Via Windows PowerShell
To retrieve the Application Process ID (PID) of a running process on Windows, PowerShell can be utilized by performing the following steps:
- Open PowerShell by clicking the Start menu, typing “PowerShell” in the search bar, and selecting “Windows PowerShell” from the search results.
- In the PowerShell window, type “Get-Process” and press Enter. This will display a list of all running processes on your system.
- Find the process for which you want to find the PID in the list, and note down the name of the process.
- In the PowerShell window, type “Get-Process -Name processname | Select-Object Id” and press Enter, replacing “processname” with the name of the process you want to find the PID for. This will display the PID number for the specified process.
- Note down the PID number for the process you are interested in.
And that’s it!
Method 5: Use Third-Party Tools
Yes, there are various third-party tools available for Windows that you can use to find the PID of a running process. Some popular examples include:
- Process Explorer – a free tool from Microsoft that provides detailed information about running processes, including the PID.
- Process Hacker – an open-source tool that offers advanced features for monitoring and managing processes, including the ability to view and filter processes by their PID.
- System Explorer – a free tool that provides a detailed overview of system processes, including their PID, CPU usage, memory consumption, and more.
These tools offer a more user-friendly and feature-rich alternative to the built-in tools like Command Prompt, Resource Monitor, and PowerShell, and can be particularly useful for advanced users or system administrators who need to monitor and manage large numbers of processes on their systems.
Also read: How To Kill Unresponsive Programs Without Task Manager
Conclusion
The Application Process ID (PID) is a unique identifier that helps to manage and monitor running processes on a Windows operating system. In this blog post, we explored several methods to find the PID of a running process, including using the Command Prompt, Resource Monitor, and PowerShell. Each of these methods has its advantages and disadvantages, and you can choose the one that works best for your needs and familiarity with the tools.
Additionally, we mentioned a few popular third-party tools that can offer advanced features and user-friendly interfaces for monitoring and managing processes on your system. By using these methods and tools, you can efficiently manage your system processes and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Did you learn something new today? Feel free to share what you think in the comments section!
